LeetCode - Sort list
Problem statement
Given the head of a linked list, return the list after sorting it in ascending order.
Problem statement taken from: https://leetcode.com/problems/sort-list
Example 1:
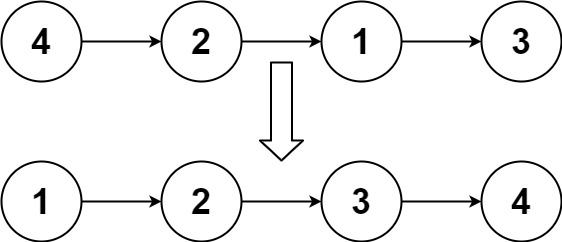
Input: head = [4, 2, 1, 3]
Output: [1, 2, 3, 4]
Example 2:
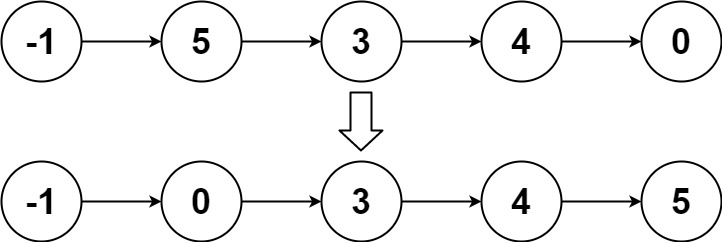
Input: head = [-1, 5, 3, 4, 0]
Output: [-1, 0, 3, 4, 5]
Example 3:
Input: head = []
Output: []
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range [0, 5 * 10^4].
- -10^5 <= Node.val <= 10^5
Explanation
MergeSort Split and Merge linked list
We can use Merge sort followed by Merge two list algorithm. In short we
- Break the list in the middle
- Recursively sort the two sub lists
- Merge the two sub lists
Let's check the algorithm to understand it better.
Algorithm
// sortList(head)
- if head == NULL || head->next == NULL
- return head
- if end
- set temp = NULL
slow = head
fast = head
- loop while fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL
- set temp = slow
slow = slow->next
fast = fast->next->next
- while end
- set temp->next = NULL
- l1 = mergeList(head)
l2 = mergeList(slow)
- return mergeList(l1, l2)
// mergeList(l1, l2)
- set ptr = new ListNode(0)
current = ptr
- loop while l1 != NULL && l2 != NULL
- if l1->val <= l2->val
- current->next = l1
- l1 = l1->next
- else
- current->next = l2
- l2 = l2->next
- if end
- current = current->next
- while end
- if l1 != NULL
- current->next = l1
- l1 = l1->next
- if end
- if l2 != NULL
- current->next = l2
- l2 = l2->next
- if end
- return ptr->next
Let's check out our solutions in C++, Golang, and Javascript.
C++ solution
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergelist(ListNode *l1, ListNode *l2) {
ListNode *ptr = new ListNode(0);
ListNode *current = ptr;
while(l1 != NULL && l2 != NULL) {
if(l1->val <= l2->val) {
current->next = l1;
l1 = l1->next;
} else {
current->next = l2;
l2 = l2->next;
}
current = current->next;
}
if(l1 != NULL) {
current->next = l1;
l1 = l1->next;
}
if(l2 != NULL) {
current->next = l2;
l2 = l2->next;
}
return ptr->next;
}
ListNode* sortList(ListNode* head) {
if(head == NULL || head->next == NULL)
return head;
ListNode *temp = NULL;
ListNode *slow = head;
ListNode *fast = head;
while(fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL) {
temp = slow;
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
temp->next = NULL;
ListNode* l1 = sortList(head);
ListNode* l2 = sortList(slow);
return mergelist(l1, l2);
}
};
Golang solution
func mergeList(l1, l2 *ListNode) *ListNode {
ptr := &ListNode{0, nil}
current := ptr
for l1 != nil && l2 != nil {
if l1.Val <= l2.Val {
current.Next = l1
l1 = l1.Next
} else {
current.Next = l2
l2 = l2.Next
}
current = current.Next
}
if l1 != nil {
current.Next = l1
l1 = l1.Next
}
if l2 != nil {
current.Next = l2
l2 = l2.Next
}
return ptr.Next
}
func sortList(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
if head == nil || head.Next == nil {
return head
}
var temp *ListNode
slow := head
fast := head
for fast != nil && fast.Next != nil {
temp = slow
slow = slow.Next
fast = fast.Next.Next
}
temp.Next = nil
l1 := sortList(head)
l2 := sortList(slow)
return mergeList(l1, l2)
}
JavaScript solution
var mergelist = function(l1, l2) {
let ptr = new ListNode(0);
let current = ptr;
while(l1 != null && l2 != null) {
if(l1.val <= l2.val) {
current.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
} else {
current.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
current = current.next;
}
if(l1 != null) {
current.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
}
if(l2 != null) {
current.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
return ptr.next;
}
var sortList = function(head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
let temp = null;
let slow = head;
let fast = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null) {
temp = slow;
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
temp.next = null;
let l1 = sortList(head);
let l2 = sortList(slow);
return mergelist(l1, l2);
};
The time complexity of the approach is O(n * log(n)). The space complexity is O(log(n)).
Let's dry-run our algorithm for a few examples to see how the solution works.
Input: head = [4, 2, 1, 3]
// sortList(head)
head -> 4 -> 2 -> 1 -> 3
Step 1: if head == NULL || head->next == NULL
head -> 4 and head->next -> 2
false
Step 2: set temp = NULL
slow = head
fast = head
slow -> 4
fast -> 4
Step 3: loop while fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL
fast -> 4 && fast->next -> 2
true
temp = slow
temp -> 4
slow = slow->next
slow -> 2
fast = fast->next->next
fast -> 1
loop while fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL
fast -> 1 && fast-next -> 3
false
temp = slow
temp -> 2
slow = slow->next
slow -> 1
fast = fast->next->next
fast -> NULL
loop while fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL
fast = NULL
false
Step 4: temp.next = NULL
temp -> 2
temp = 4 -> 2 -> NULL
Step 5: l1 = sortList(head)
head = 4 -> 2 -> NULL
// sortList(head)
head -> 4 -> 2 -> NULL
Step 6: if head == NULL || head->next == NULL
head -> 4 and head->next -> 2
false
Step 7: set temp = NULL
slow = head
fast = head
slow -> 4
fast -> 4
Step 8: loop while fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL
fast -> 4 && fast->next -> 2
true
temp = slow
temp -> 4
slow = slow->next
slow -> 2
fast = fast->next->next
fast -> NULL
loop while fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL
fast = NULL
false
Step 9: temp.next = NULL
temp -> NULL
temp = 4 -> NULL
Step 10: l1 = sortList(head)
head = 4 -> NULL
// sortList(head)
head -> 4 -> NULL
Step 11: if head == NULL || head->next == NULL
head -> 4 || head->next -> NULL
true
return head
We rollback to Step 10 and evaluate next line
Step 12: l2 = sortList(slow)
slow = 2 -> NULL
// sortList(head)
head -> 2 -> NULL
Step 13: if head == NULL || head->next == NULL
head -> 2 || head->next -> NULL
true
return head
We rollback to Step 12 and evaluate next line
Step 14: return mergelist(l1, l2)
l1 = 4 -> NULL
l2 = 2 -> NULL
// mergelist(l1, l2)
Step 15: ptr = new ListNode(0)
= 0 -> NULL
current = 0 -> NULL
Step 16: loop while l1 != NULL && l2 != NULL
l1 -> 4
l2 -> 2
true
if l1->val <= l2->val
4 <= 2
false
else
current->next = l2
current = 0 -> 2
l2 = l2->next
l2 = NULL
current = current->next
= 2 -> NULL
loop while l1 != NULL && l2 != NULL
l1 -> 4
l2 -> NULL
false
Step 17: if l1 != NULL
4 != NULL
true
current->next = l1
current = 2 -> 4 -> NULL
l1 = l1->next
= NULL
Step 18: if l2 != NULL
NULL != NULL
false
Step 19: ptr->next
ptr = 0 -> 2 -> 4 -> NULL
ptr->next = 2 -> 4 -> NULL
We follow the algorithm for the rest of the list and return the answer as
1->2->3->4->NULL