LeetCode - Count Good Nodes in Binary Tree
Problem statement
Given a binary tree root, a node X in the tree is named good if in the path from root to X there are no nodes with a value greater than X.
Return the number of good nodes in the binary tree.
Problem statement taken from: https://leetcode.com/problems/kth-smallest-element-in-a-sorted-matrix
Example 1:
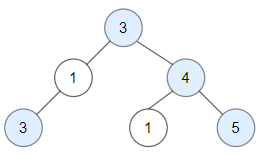
Input: root = [3, 1, 4, 3, null, 1, 5]
Output: 4
Explanation: Nodes in blue are good.
Root Node (3) is always a good node.
Node 4 -> (3, 4) is the maximum value in the path starting from the root.
Node 5 -> (3, 4, 5) is the maximum value in the path
Node 3 -> (3, 1, 3) is the maximum value in the path.
Example 2:
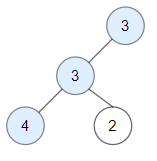
Input: root = [3, 3, null, 4, 2]
Output: 3
Explanation: Node 2 -> (3, 3, 2) is not good, because '3' is higher than it.
Example 3:
Input: root = [1]
Output: 1
Explanation: Root is considered as good.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the binary tree is in the range [1, 10^5].
- Each node's value is between [-10^4, 10^4].
Explanation
DFS recursion
It's one of the easiest problem on LeetCode. We recursively iterate over the tree and keep track of the maximum value in each iteration. We consider the node if it's greater than the parent node.
Let's check the algorithm for this approach.
Algorithm
// goodNodes function
- return dfs(root)
// dfs function
- if root == NULL
- return 0
- return (root->val >= maximumTillNow ? (maximumTillNow = root->val, 1) : 0) +
dfs(root->left, maximumTillNow) +
dfs(root->right, maximumTillNow)
The time complexity of this approach is O(n) and space complexity is O(n * log(n)).
C++ solution
class Solution {
public:
int dfs(TreeNode* root, int maximumTillNow = INT_MIN) {
if(root == NULL) {
return 0;
}
return (root->val >= maximumTillNow ? (maximumTillNow = root->val, 1) : 0) +
dfs(root->left, maximumTillNow) +
dfs(root->right, maximumTillNow);
}
int goodNodes(TreeNode* root) {
return dfs(root);
}
};
Golang solution
func dfs(root *TreeNode, maximumTillNow int) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
addCount := 0
if root.Val >= maximumTillNow {
maximumTillNow = root.Val
addCount = 1
}
return addCount + dfs(root.Left, maximumTillNow) + dfs(root.Right, maximumTillNow)
}
func goodNodes(root *TreeNode) int {
return dfs(root, math.MinInt)
}
JavaScript solution
var dfs = function(root, maximumTillNow) {
if(root === null) {
return 0;
}
let addCount = 0;
if(root.val >= maximumTillNow) {
maximumTillNow = root.val;
addCount = 1;
}
return addCount + dfs(root.left, maximumTillNow) + dfs(root.right, maximumTillNow);
}
var goodNodes = function(root) {
return dfs(root, root.val)
};
Let's dry-run our algorithm to see how the solution works.
Input: root = [3, 1, 4, 3, null, 1, 5]
// goodNodes function
Step 1: return dfs(root)
root -> 3
// dfs function
Step 2: if root == NULL
root -> 3
false
root->val >= maximumTillNow
3 >= INT_MIN
true
maximumTillNow = root->val
= 3
return (root->val >= maximumTillNow ? (maximumTillNow = root->val, 1) : 0) +
dfs(root->left, maximumTillNow) +
dfs(root->right, maximumTillNow)
return 1 + dfs(1, 3) + dfs(4, 3)
// dfs(1, 3)
Step 3: if root == NULL
root -> 1
false
root->val >= maximumTillNow
1 >= 3
false
return (root->val >= maximumTillNow ? (maximumTillNow = root->val, 1) : 0) +
dfs(root->left, maximumTillNow) +
dfs(root->right, maximumTillNow)
return 0 + dfs(3, 3) + dfs(null, 3)
// dfs(3, 3)
Step 4: if root == NULL
root -> 3
false
root->val >= maximumTillNow
3 >= 3
true
maximumTillNow = root->val
= 3
return (root->val >= maximumTillNow ? (maximumTillNow = root->val, 1) : 0) +
dfs(root->left, maximumTillNow) +
dfs(root->right, maximumTillNow)
return 1 + dfs(null, 3) + dfs(null, 3)
dfs(null, 3) returns 0
We return 1 + 0 + 0 = 1
We backtrack to Step 3
// dfs(1, 3)
Step 5: return 0 + dfs(3, 3) + dfs(null, 3)
0 + 1 + 0
return 1
We backtrack to Step 2
// dfs(3, INT_MIN)
Step 6: return 1 + dfs(1, 3) + dfs(4, 3)
1 + 1 + dfs(4, 3)
// dfs(4, 3)
Step 7: if root == NULL
root -> 4
false
root->val >= maximumTillNow
4 >= 3
true
maximumTillNow = root->val
= 4
return (root->val >= maximumTillNow ? (maximumTillNow = root->val, 1) : 0) +
dfs(root->left, maximumTillNow) +
dfs(root->right, maximumTillNow)
return 1 + dfs(1, 4) + dfs(5, 4)
// dfs(1, 4)
Step 8: if root == NULL
root -> 1
false
root->val >= maximumTillNow
1 >= 4
false
return (root->val >= maximumTillNow ? (maximumTillNow = root->val, 1) : 0) +
dfs(root->left, maximumTillNow) +
dfs(root->right, maximumTillNow)
return 0 + dfs(null, 4) + dfs(null, 4)
dfs(null, 4) returns 0
We return 0 + 0 + 0 = 0
We backtrack to Step 7
// dfs(4, 3)
Step 9: return 1 + dfs(1, 4) + dfs(5, 4)
1 + 0 + dfs(5, 4)
// dfs(5, 4)
Step 10: if root == NULL
root -> 5
false
root->val >= maximumTillNow
5 >= 4
true
maximumTillNow = root->val
= 5
return (root->val >= maximumTillNow ? (maximumTillNow = root->val, 1) : 0) +
dfs(root->left, maximumTillNow) +
dfs(root->right, maximumTillNow)
return 1 + dfs(null, 5) + dfs(null, 5)
dfs(null, 5) returns 0
We return 1 + 0 + 0 = 1
We backtrack to Step 9
// dfs(4, 3)
Step 11: return 1 + 0 + dfs(5, 4)
1 + 0 + 1
2
We backtrack to Step 9
// dfs(4, 3)
Step 12: return 1 + 0 + dfs(5, 4)
1 + 0 + 1
2
We backtrack to Step 6
// dfs(3, INT_MIN)
Step 13: return 1 + 1 + dfs(4, 3)
1 + 1 + 2
4
// goodNodes
Step 14: return dfs(root)
4
We return the answer as 4.