LeetCode - Binary Tree Right Side View
Problem statement
Given the root of a binary tree, imagine yourself standing on the right side of it, return the values of the nodes you can see ordered from top to bottom.
Problem statement taken from: https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-tree-right-side-view
Example 1:
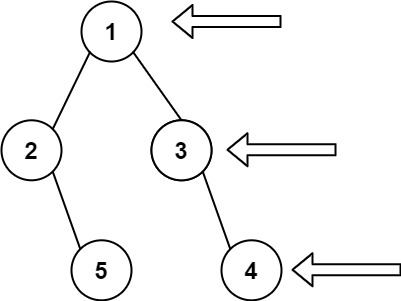
Input: root = [1, 2, 3, null, 5, null, 4]
Output: [1, 3, 4]
Example 2:
Input: root = [1, null, 3]
Output: [1, 3]
Example 3:
Input: root = []
Output: []
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [0, 100].
- -100 <= Node.val <= 100
Explanation
The problem can be solved using PostOrder traversal or Level order traversal. Let's explore the Level order traversal using queues.
Level order traversal
We have explored level order traversal using both recursion and iterative approach in our previous blog post LeetCode - Binary Tree Level Order Traversal
Let's use the iterative approach and check the algorithm first.
- if root == NULL
- return {}
- initialize queue<TreeNode*> q
push root q.push(root)
- initialize vector<int> result
int queueSize, i
- loop while !q.empty()
- set queueSize = q.size()
- loop for i = queueSize; i > 0; i--
- set node = q.front()
- q.pop()
- if i == queueSize
- result.push_back(node->val)
- if node->right != NULL
- q.push(node->right)
- if node->left != NULL
- q.push(node->left)
- end for loop
- end while loop
- return result
The time complexity of the above approach is O(n), and the space complexity is O(n).
Let's check our algorithm in C++, Golang, and Javascript.
C++ solution
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> rightSideView(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == NULL) {
return {};
}
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
vector<int> result;
int queueSize, i;
while(!q.empty()) {
queueSize = q.size();
for(i = queueSize; i > 0; i--) {
TreeNode* node = q.front();
q.pop();
if(i == queueSize) {
result.push_back(node->val);
}
if(node->right != NULL) {
q.push(node->right);
}
if(node->left != NULL) {
q.push(node->left);
}
}
}
return result;
}
};
Golang solution
func rightSideView(root *TreeNode) []int {
if root == nil {
return []int{}
}
queue := []*TreeNode{root}
result := []int{}
queueSize, i := 0, 0
var node *TreeNode
for len(queue) != 0 {
queueSize = len(queue)
for i = queueSize; i > 0; i-- {
node = queue[0]
queue = queue[1:]
if i == queueSize {
result = append(result, node.Val)
}
if node.Right != nil {
queue = append(queue, node.Right)
}
if node.Left != nil {
queue = append(queue, node.Left)
}
}
}
return result
}
Javascript solution
var rightSideView = function(root) {
if(root == null) {
return [];
}
let queue = [root];
let result = [];
let queueSize = 0, i = 0;
let node;
while(queue.length > 0 ) {
queueSize = queue.length;
for(i = queueSize; i > 0; i--) {
node = queue.shift();
if(i == queueSize) {
result.push(node.val);
}
if(node.right != null) {
queue.push(node.right);
}
if(node.left != null) {
queue.push(node.left);
}
}
}
return result;
};
Let's dry-run our algorithm to see how the solution works.
Input: root = [1, 2, 3, null, 5, null, 4]
Step 1: if root == NULL
root -> 1
false
Step 2: queue<TreeNode*> q
q.push(root)
q = [1]
Step 3: vector<int> result
int queueSize, i
Step 4: loop while(!q.empty())
!q.empty() = true
queueSize = q.size()
= 1
loop for i = queueSize; i > 0; i--
i = 1
1 > 0
true
node = q.front()
= ->1
q.pop()
q = []
if i == queueSize
1 == 1
true
result.push_back(q->val)
result.push_back(1)
result = [1]
if node->right != NULL
node->right = ->3
true
q.push(node->right)
q.push(->3)
q = [3]
if node->left != NULL
node->left = ->2
true
q.push(node->right)
q.push(->2)
q = [3, 2]
i--
i = 0
for i > 0
0 > 0
false
Step 5: loop while(!q.empty())
!q.empty() = true
queueSize = q.size()
= 2
loop for i = queueSize; i > 0; i--
i = 2
2 > 0
true
node = q.front()
= ->3
q.pop()
q = [2]
if i == queueSize
2 == 2
true
result.push_back(q->val)
result.push_back(3)
result = [1, 3]
if node->right != NULL
node->right = ->4
true
q.push(node->right)
q.push(->4)
q = [2, 4]
if node->left != NULL
NULL != NULL
false
i--
i = 1
loop for i > 0
1 > 0
true
node = q.front()
= ->2
q.pop()
q = [4]
if i == queueSize
1 == 2
false
if node->right != NULL
node->right = ->5
true
q.push(node->right)
q.push(->5)
q = [4, 5]
if node->left != NULL
NULL != NULL
false
i--
i = 0
loop for i > 0
0 > 0
false
Step 6: loop while(!q.empty())
!q.empty() = true
queueSize = q.size()
= 2
loop for i = queueSize; i > 0; i--
i = 2
2 > 0
true
node = q.front()
= ->4
q.pop()
q = [5]
if i == queueSize
2 == 2
true
result.push_back(q->val)
result.push_back(4)
result = [1, 3, 4]
if node->right != NULL
NULL != NULL
false
if node->left != NULL
NULL != NULL
false
i--
i = 1
loop for i > 0
1 > 0
true
node = q.front()
= ->5
q.pop()
q = []
if i == queueSize
1 == 2
false
if node->right != NULL
NULL != NULL
false
if node->left != NULL
NULL != NULL
false
i--
i = 0
loop for i > 0
0 > 0
false
Step 7: loop while(!q.empty())
!q.empty() = false
q = []
Step 8: return result
We return the answer as [1, 3, 4].